Learning the Different Parts of a Sailboat: A Complete Guide for Beginners
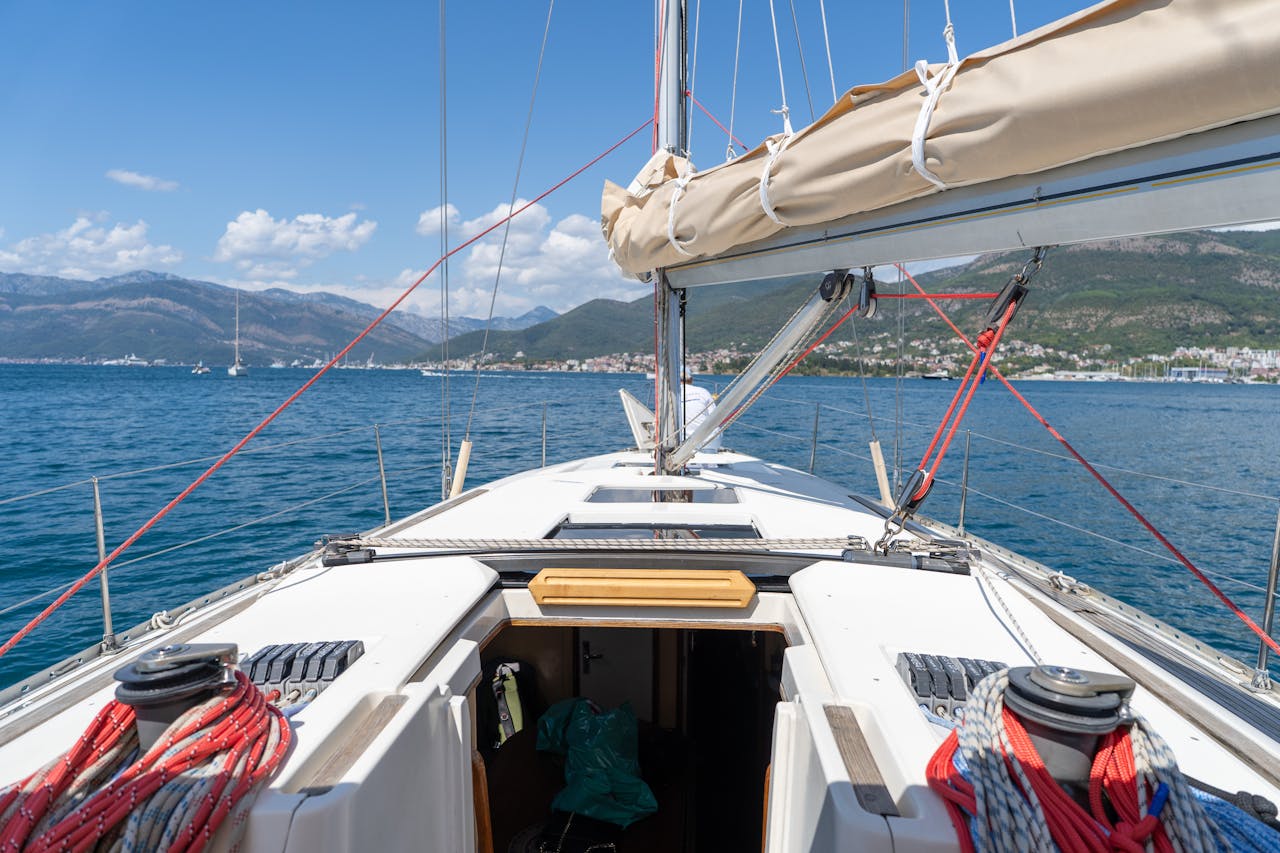
1. The Hull: The Body of the Sailboat
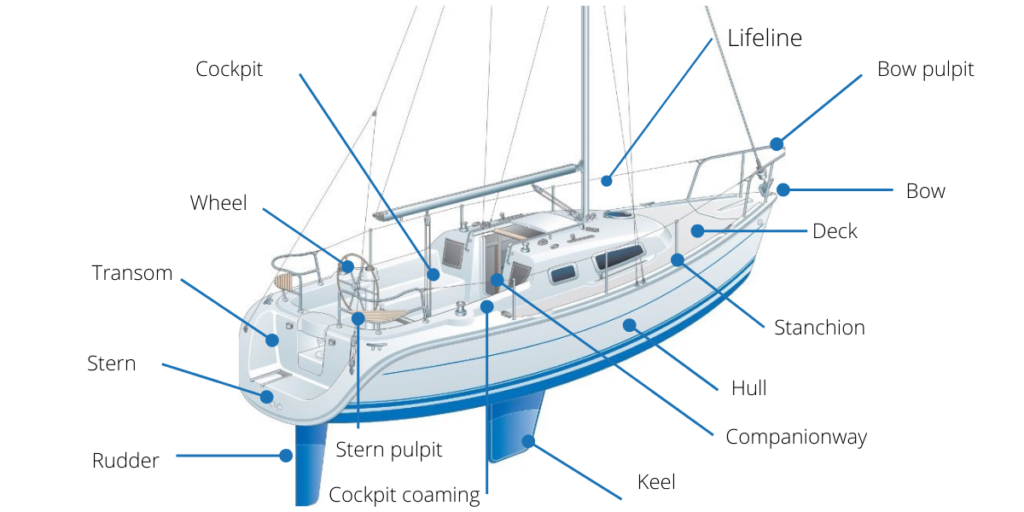
The hull is the main body of the sailboat. Everything on the boat attaches to the hull, and it gives the vessel its shape, stability, and buoyancy.
Key Areas of the Hull
Bow – the front of the boat- Stern – the back of the boat
- Port – the left side (when facing forward)
- Starboard – the right side
The hull may be made of fiberglass, wood, aluminum, or steel.
2. Deck and Cockpit
Deck
The deck is the flat surface on top of the hull where sailors move around. It provides access to sails, rigging, and safety equipment.
Cockpit
The cockpit is the seating area where the crew steers and manages the boat.
This is often where the helm, instruments, and engine controls are located.
3. Mast, Boom, and Standing Rigging
These parts form the “skeleton” that holds the sails up.
Mast
The mast is the tall vertical pole rising from the deck that supports the sails. Boats may have one mast (sloop) or multiple masts (ketch, yawl, schooner).
Boom
The boom is the horizontal pole at the bottom of the mainsail. It helps control sail shape and direction.
Standing Rigging
These are the fixed wires that hold the mast upright:
Forestay – supports the mast forward- Backstay – supports the mast backward
- Shrouds – supports the mast from side to side
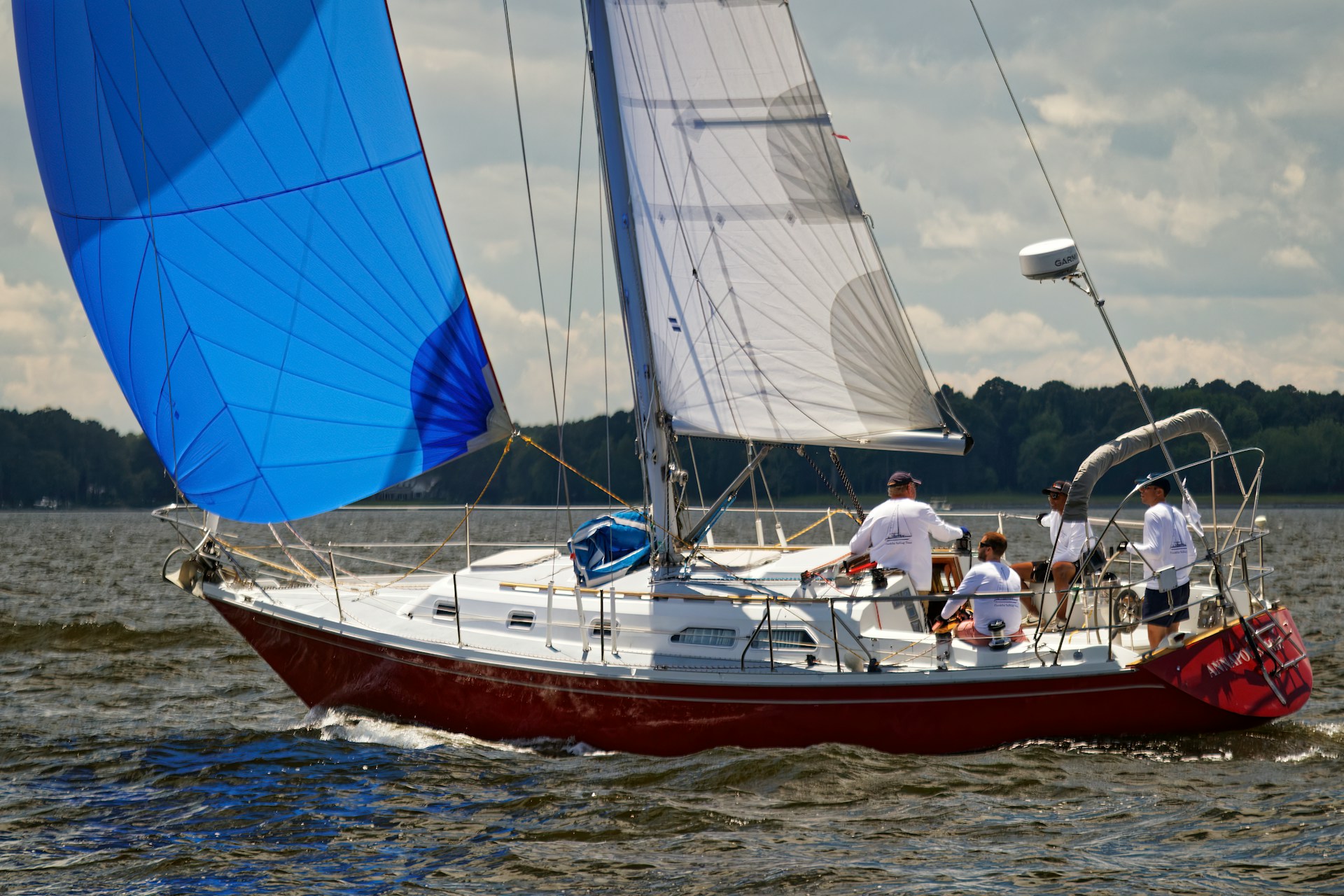
4. Sails: The Engine of a Sailboat
Sails capture wind to propel the boat.
The largest sail, attached to the mast and the boom.
Jib or Headsail
A smaller sail at the front of the boat, attached to the forestay.
Genoa
A larger version of the jib that overlaps the mast for more power.
Spinnaker
A large, balloon-shaped sail used when sailing downwind.
5. Running Rigging: Lines That Control the Sails
Running rigging includes all the ropes and lines used to adjust the sails.
Important Lines:
Halyards – raise and lower the sails- Sheets – control the angle of the sails
- Outhaul – tightens the foot of the mainsail
- Downhaul/Cunningham – adjusts sail tension
- Vang – controls the boom height and sail shape
In sailing, ropes are always called lines.
6. Keel, Centerboard, or Daggerboard
These components keep the sailboat stable and prevent sideways sliding (called “leeway”).
Keel
A heavy fixed fin under the boat, often weighed with lead.
Centerboard or Daggerboard
Retractable fins used on smaller sailboats.
These structures also help the boat sail upwind.
7. Rudder and Steering System
Rudder
A vertical blade under the stern used for steering.
Tiller or Wheel
Tiller – a handle connected to the rudder- Wheel – a helm used to control larger sailboats
Both systems turn the rudder to steer the boat.
8. Cabin, Berths, and Interior Spaces
On larger sailboats, interior spaces include:
Cabin – enclosed area under the deck- V-berth – sleeping area in the bow
- Galley – kitchen
- Head – bathroom
- Saloon – main living or dining area
Small sailboats may not have sleeping or interior spaces.
9. Winches, Cleats, and Hardware
Winches
Mechanical drums that help pull in heavy lines.
Cleats
Fittings used to secure lines.
Blocks
Pulleys that allow lines to move smoothly.
These components make sail handling easier and safer.
10. Safety and Navigation Equipment
Every sailboat should carry:
Life jackets- Anchor and rode
- VHF radio
- Navigation lights
- Fenders
- Bilge pump
- Emergency flares
- GPS or chart plotter
Safety gear is just as important as the sails and rigging.
Why Understanding Sailboat Parts Matters
Knowing sailboat terminology helps sailors:
Communicate clearly on the water- Handle sails and rigging safely
- Troubleshoot mechanical issues
- Understand weather and wind effects
- Become more confident boat operators
Whether you're buying, selling, or learning to sail, knowledge is your most powerful tool.
.png)